HAS-BLED Score utvecklades för att skatta risken för allvarliga blödningar (major bleeding: intracranial, hospitalization, hemoglobin decrease 2 g/L, and/or transfusion) inom 1 år hos patienter med förmaksflimmer som behandlas med oral antikoagulation. 1 Datan kommer från ca 4000 patienter i Euro Heart Survey.
Användning av HAS-BLED (för patienter med förmaksflimmer) rekomenderas i ESC guideline förmaksflimmer 2020 2 och ESC update DAPT 2017 3 4
Sidoinnehåll
HAS-BLED score
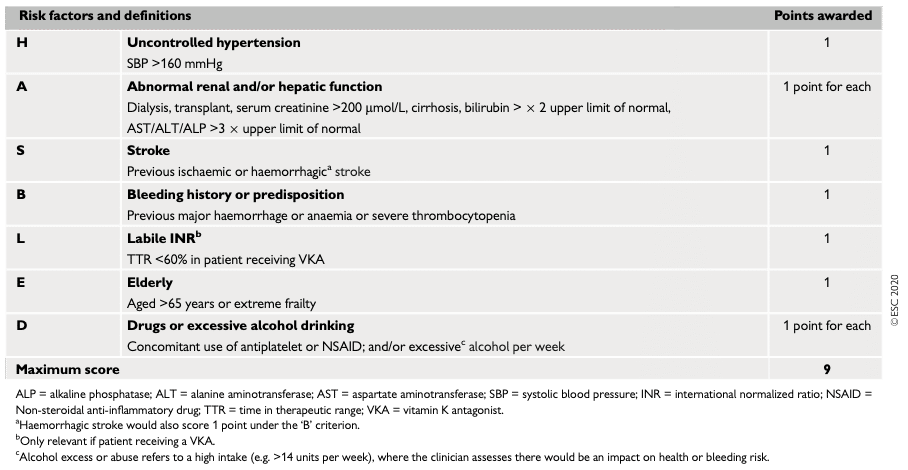
| Riskfaktor | Poäng | |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hypertoni Okontrollerad hypertoni, systoliskt blodtryck >160 mmHg (obs: hypertoni som är behandlad och välreglerad ger INTE poäng) | 1 |
| A | Onormal njur- eller leverfunktion (1 poäng vardera) Dialys, njurtransplanterad, kreatinin > 200 mmol/L Cirrhos eller Vilirubin >2 ggr övre referensen, samtidigt ASAT/ALAT >3 ggr övre referensen) | 1-2 |
| S | Stroke Tidigare stroke, särskilt lakunär | 2 |
| B | Blödning Blödning i anamnesen eller predisposition (t.ex. misstänkt blödningsanemi) | 1 |
| L | Instabilt INR (therapeutic time in range <60 %) | 1 |
| E | Ålder >65 år | 1 |
| D | Läkemedel och alkohol (1 poäng vardera) Läkemdel=Trombocytantagonister (Trombyl eller Clopidogrel eller andra), eller NSAID Alkohol: ≥ 8 enheter/vecka | 1-2 |
| Summa | 0-9 |
HAS-BLED score: ESC tabell
Interpretation:
≥ 3 poäng = hög blödningsrisk
Litteratur
ESC guideline förmaksflimmer 2020 2
Last Updated on July 12, 2021 by Christian Dworeck
Latest posts by Christian Dworeck (see all)
- Ny sida om isoprenalin - February 16, 2023
- Ny sida: ST-handledning - December 27, 2022
- Nytt EKG-exempel på sidan esofagus-EKG - November 5, 2022
Referenser
- Pisters R, Lane DA, Nieuwlaat R, de Vos CB, Crijns HJ, Lip GY. A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro Heart Survey. Chest. 2010;138(5):1093-1100. doi:10.1378/chest.10-0134[↩]
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Boriani G, Castella M, Dan GA, Dilaveris PE, Fauchier L, Filippatos G, Kalman JM, La Meir M, Lane DA, Lebeau JP, Lettino M, Lip GYH, Pinto FJ, Thomas GN, Valgimigli M, Van Gelder IC, Van Putte BP, Watkins CL; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):373-498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):507. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):546-547. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):541-543. PMID: 32860505.[↩][↩]
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(38):2893-2962. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehw210[↩]
- Valgimigli M, Bueno H, Byrne RA, et al. 2017 ESC focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with EACTS: The Task Force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J. 2018;39(3):213–260. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehx419[↩]

